HOW SATURATED FATS CAN BE DETRIMENTAL TO OUR HEALTH
It's never been a more important time to reduce our saturated fat intake to help with the prevention of chronic diseases such as heart disease.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that a diet high in saturated fats can increase the risk of developing heart disease and other chronic health conditions by contributing to higher levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, which is commonly known as "bad" cholesterol.
It is, therefore, advisable to limit the consumption of saturated fats in one's diet and opt for healthier alternatives such as monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fats, which can be found in plant-based foods.
Incorporating these healthier fat sources into one's daily meals not only supports overall health and well-being but also aids in the prevention of numerous cardiovascular and metabolic diseases, thus emphasizing the importance of making mindful choices when it comes to dietary habits.
WHAT ABOUT OILS?
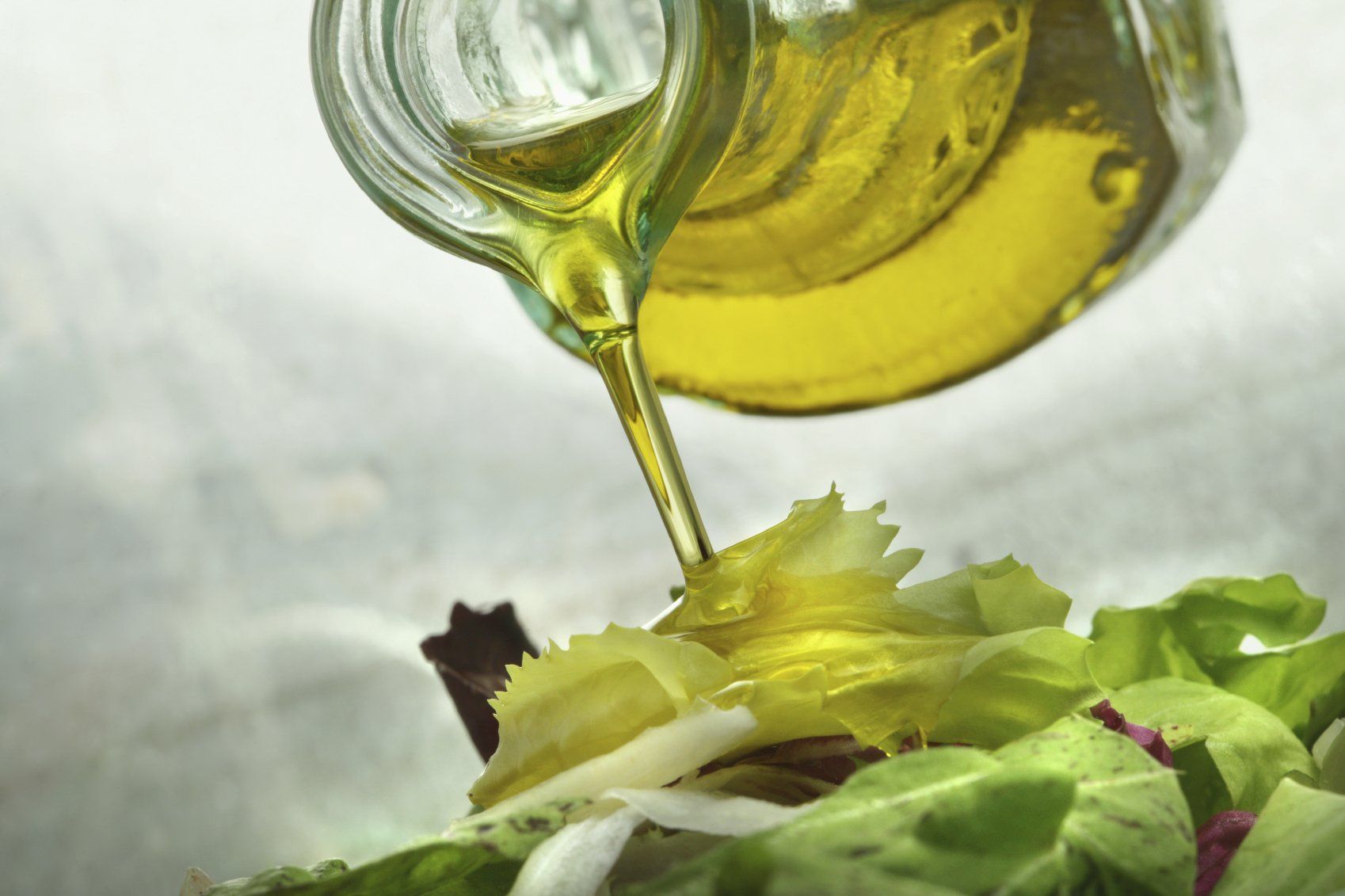
You might have learned that oils are often thought of as good for your health, with olive oil being particularly popular. It's commonly known that the Mediterranean diet places emphasis on using oils for their nutritional benefits. However, it's important to note that no type of oil - be it coconut, olive, grapeseed or any other kind - can truly be classified as a "health food".
It is imperative to acknowledge that the processing of most oils follows a procedure analogous to that of sugar. The refining process leads to the removal of nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals in addition to healthy fats inherent in olives, resulting in an oil with a high concentration of fat. Although minute traces of certain essential nutrients may remain within these oils, their nutritional worth does not compare favourably with whole foods which provide saturated and unsaturated fats alongside other vital nutrients.
As we know the pre-westernised Mediterranean diet is considered healthy because they mostly consist of plant-based foods. This includes fruits and vegetables, whole grains and cereals, legumes, and nuts. On the other hand, these diets have low amounts of red meat, dairy products and sweets which make them healthier overall compared to western animal-heavy and processed food diets. Despite high intake of olive oil in this kind of diet which may cause some harm; consumption of these nutritious plant-based foods seem to counteract its negative effects making it still beneficial for our health.
It can be contended that oil is comparable to processed sugar in terms of being composed mostly of empty calories. Additionally, the findings from an essential investigation conducted by Dr. Robert Vogel at the University of Maryland and published in American Cardiology Journal
(1)
revealed that consumption of olive oil resulted in reduced blood flow within arteries by 31%, which holds considerable significance regarding heart attacks and blood clots. The study also discovered that ingestion of olive oil inflicted significant harm on endothelial cells situated along arterial interiors causing inflammation and tears within arterial walls thus leading to atherosclerosis.
HEART DISEASE - A GLOBAL HEALTH CRISIS
The buildup of plaque containing cholesterol in the arterial walls that provide blood to the heart is responsible for Coronary Heart Disease. This condition causes a narrowing of artery interiors over time referred to as atherosclerosis. Failure to treat this can result in serious consequences such as developing Coronary Heart Disease; hence maintaining a healthy diet with limited saturated fat intake becomes crucial. Considering that it remains one of the most significant global health concerns causing mortality, adhering strictly to dietary modifications supporting cardiac function must be considered paramount for individuals worldwide.
The concern at hand pertains not only to oils, but also to animal-derived saturated fats that can contribute similarly towards arterial afflictions. Oils are particularly noteworthy due to their high caloric density of 14 grams per tablespoon primarily composed of fat - a nutritional attribute exceeding other food sources. Increased consumption of foods rich in saturated fat has been linked with elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), which increases susceptibility for developing heart disease and type-2 diabetes.
Unhealthy fats are those that solidify when exposed to ambient temperature, specifically saturated and trans fats. It is advisable to decrease the intake of saturated fat while avoiding trans fat altogether. These types of unhealthy lipids can be present in various animal and plant products, leading to increased vulnerability towards heart disease due to elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels along with reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels.
Saturated fats are found in various animal-based products such as meat, butter, eggs, and dairy, as well as some plant-derived sources such as coconut oil and palm oil which are commonly added to processed foods.
Saturated Fats
- Butter and margarine, both dairy and non-dairy
- Coconut oil
- Palm oil, palm oil containing products
- Processed foods, such as biscuits, cakes, pastries, pies, meat replacements and take away foods
- Meat and meat products
- Ice-cream, both dairy and non-dairy
Trans fats are naturally found in some animal-based foods such as meat, dairy, butter, eggs and some meat products. Trans fats are also consumed by processed foods which .
Trans Fat
- Deep-fried foods
- Biscuits, Cakes and Pastries
- Butter, from dairy
- Breads, commercially baked
- Take away foods such as Burgers, Pizza and Chips
- Foods that list 'Hydrogenated Oil' or 'Partially Hydrogenated Vegetable Oils' on the ingredients list.
Trans fatty acids, present in hydrogenated and partially hydrogenated vegetable oil, have been found to be up to 10 times more detrimental to heart health than saturated fats. These unhealthy components are commonly present in a wide range of processed foods such as bread, cakes, biscuits, microwave popcorns, margarine spreads, chocolates and ready-to-eat meals.
WHICH FATS ARE GOOD?
The fats we need can be obtained from whole food sources such as avocados, nuts, and seeds, rather than relying on processed oils that provide minimal nutritional value compared to their whole food counterparts.
Unsaturated fats, found in plant-based sources like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are crucial for the human body's energy requirements and various essential processes such as absorbing specific vitamins and minerals. These unsaturated fats possess a beneficial impact on health by decreasing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels along with improving artery function
Monounsaturated Fats
Research shows that consumption of plant-based monounsaturated fats may help lower your risk for cardiovascular disease and overall mortality.
Foods that are highest in monounsaturated fats include:
- Avocados
- Olives
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Peanuts
- Brazil nuts
- Hazelnuts
- Sesame seeds
Polyunsaturated Fats
Your body needs polyunsaturated fats to function. Polyunsaturated fats help with muscle movement and blood clotting. Since your body doesn’t make this type of fat, you have to get it through your diet.
Polyunsaturated fats can be further divided into two types: omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
Omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for heart health.
The best sources of plant-based omega-3 fatty acids are:
- Ground flax
- Soybeans/ Edamame/ Tofu
- Squash/ Pumpkin
- Black beans/ Kidney beans
- Walnuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Chia seeds
- Hemp seeds
WHAT ABOUT OMEGA-3?
Fish although containing omega-3 fats that the fish have converted for themselves via ALA also contain high levels of saturated fat, unsafe levels of environmental dioxins
(2), and heavy metals, all which can be avoided by opting for plant-based sources of omega-3.
The idea is that a diet of fish and blubber - not vegetables and fruits - has kept Arctic natives free of heart disease is a myth that has been busted.
(3)
Controlled studies, have failed to show benefits of fish oil. In a 2012 report in the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers compiled the results of 20 studies including 68,680 patients, finding that fish oil had no effect on heart-related deaths, heart attacks, or strokes.
(4)
Coming back to plants which are low in fat, however the fats they do contain alongside the natural plant omega-3 sources actually help to perfect the ratio for ALA to convert to DHA and EPA. The more saturated fats in the diet make this conversion difficult, making you absorb less omega-3.
(5)
The key here is to consume a whole food plant-based diet low in fat and including healthy sources of unsaturated fat sand avoiding trans and saturated fats where possible.
HOW TO REDUCE SATURATED FAT AND OIL CONSUMPTION
- Preparing your foods from scratch.
- Swapping unhealthy fats for healthy fats.
- Using oil-free methods of cooking.
- Switching animal protein sources for plant-based protein sources.
- Reducing processed labelled foods that contain added fat/oils.
END POINT
To promote better health, it is advisable to make adjustments in our food choices and cooking techniques by refraining from the intake of animal fats, oils and processed foods. These types of consumables are rich in fat calories which can be deleterious to one's physical wellbeing as they heighten susceptibility to ailments such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Instead, it is recommended that individuals prioritise the consumption of whole plant-based foods as they offer high levels of essential nutrients and healthier fat alternatives.
Thanks for reading!
Article by Rose Wyles - The Vegan Nutritionist
For professional assistance in adopting a healthy and nutritious plant-based diet, kindly reach out to me using the form provided below. I can help you address any possible nutrient deficiencies or health concerns and ensure that your nutritional needs are met through the consumption of plant-based foods.
Additionally, use my services to create a customised plan for reaching your health and wellness goals which includes personalised meal plans, nutritional advice, tasty plant-based recipes, and more.
Start your journey to better health and wellness today!
REFERENCES